Air Gap Overflow Fitting (Rain Harvesting)
The Air Gap is an essential element in any Rain Harvesting system where your overflows are plumbed into stormwater. Air gaps prevent stormwater backflow from entering your rainwater tank and lowering your water quality. They also create a visual inspection point for detecting any overflow issues and stop mosquitoes and other vermin from entering your rainwater tank.Price $30.00 – $62.00 GST incl.
| Brand | Rain Harvesting |
|---|---|
| Pipe Fitting | 90mm Female (TAAG01) / 100mm Female (TAAG02) |
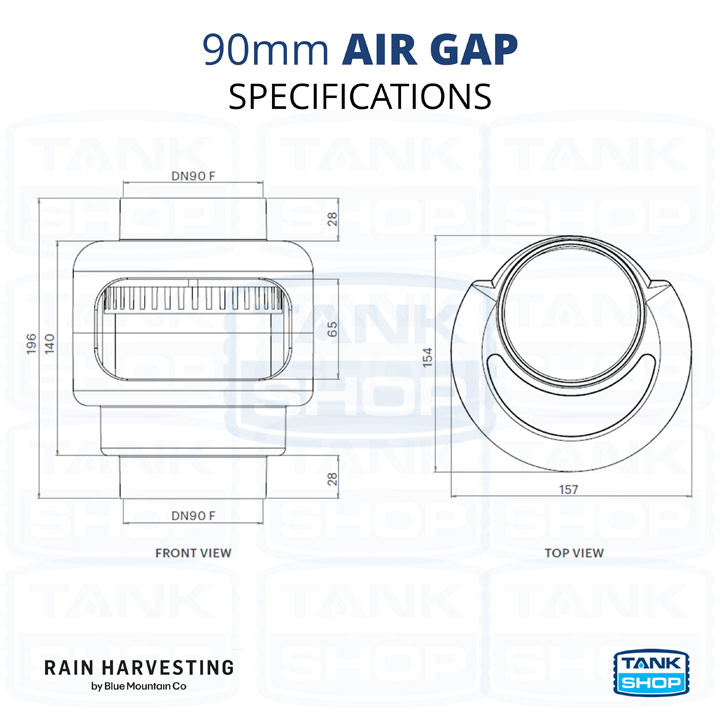
90mm Air Gap Installation & Specification Guide
100mm Air Gap Installation & Specification Guide.
The Air Gap is an essential element in any Rain Harvesting system where your overflows are plumbed into stormwater. Air gaps prevent stormwater backflow from entering your rainwater tank and lowering your water quality. They also create a visual inspection point for detecting any overflow issues and stop mosquitoes and other vermin from entering your rainwater tank.
How does the Air Gap prevent backflow?
In an extreme rainfall event there is the possibility that if your overflow is plumbed into your stormwater, water could potentially flow back up your stormwater overflow pipe and into your rainwater tank.
If your local stormwater infrastructure (beyond your property boundary) becomes blocked, the system can “charge”, causing dirty stormwater to surge back through your stormwater pipework. If your rainwater tank overflow is connected to stormwater, this “charged” stormwater can backup into the tank.
If the pipes connected to the overflow of the rainwater tank are crushed, excess water from any pipework connected to the same system could flow back towards the tank, taking with them whatever debris is in the system.
If your tank is going to a soakage pit, in an extreme rain event the pit could become saturated and water can flow back up towards the
An air gap prevents this problem by creating a physical gap between your rainwater tank and stormwater lines. With an air gap, overflowing stormwater is prevented from backing up into your tank. Instead, it will spill out through the front of your air gap.
How to Install an Air Gap (90mm or 100mm version)
Cleaning & Maintaining Your Air Gap
90mm Air Gap Installation & Specification Guide
100mm Air Gap Installation & Specification Guide
We strive to provide you with a smooth and easy buying experience from order to delivery.
Here are some kind words from happy customers:
Thanks for the excellent customer service, especially that the order wasn't a straight forward one. I'd highly recommend you guys if someone asked about tanks, particularly stainless steel ones.
Great Service - Very commutative throughout the whole. However best for us, was the flexibility to work around our plumber. We changed delivery dates three times and they were easy to work with and even worked with our plumber direct, as a result tank delivered and fitted all the same day.
Fantastic price, customer service & product! We bought a QTank poly-slimline tank via Tank Shop, for our pool/garden. The customer service, delivery and quality of the product was fantastic. We’ve had a lot of trades & deliveries during our renovations and the experience with QTank and Tank Shop was one of the best. They were quick to confirm everything, kept us informed throughout and the QTank delivery was super smooth and well explained. Would highly recommend both companies.
No worries at all Tank shop were simply great.
Lotsa detailed help.
Careful and effective.
Actually surprisingly cheap for stainless.
Beautiful tank, I mean real pretty.
Delivery bloke was superb, even helping me with getting around a tight corner I should have had ready, with only positivity.
Oh and only a week and a half from order to install. This is not usual, but still, it happened.
Couldn’t be happier. It even rained after the install.
Great service Tank Shop staff were excellent to deal with and found a great solution for my installation. Price was good, service was great and I was kept informed of where my order was up to every step of the way. Delivery was right on time and the guys installing the tanks were very good. Highly recommend Tank Shop to anyone!
The process throughout has gone very smoothly - from the excellent information provided by you guys before and during the order process, through to the frequent updates and punctual delivery by Kingspan.
It's been a great experience - I will be happily recommending you to any of my colleagues who are looking for a tank.
Thanks for all your help!
Very happy and pleased with service, reliability and generous assistance. Have recommended Tank Shop to friends already. Thank you, Scott, for a very good experience you provided for us, your generous assistance at any time, your reliability and very good service.
Great service, price and excellent communications. More than happy to recommend the Tank Shop
Very attentive and fully laid out pathway from enquiry to delivery... and even the delivery man was good value.
We had a very good experience with the purchase of our tank. All questions were answered promptly and the order process was very easy.
My plumber completed the install and was very happy with the product and the delivery. Thank you.
Scott was very helpful in answering questions about the installation of the leaf guards and always returned my calls.
Would Recommend ... Nice Tank, Delivered Within a Week, Great Service, Good Value ... Perfect A1 +++++ ... Thank You :)
Prompt friendly timely comprehensive service providing good value for money 5,000L tank.
Ordered online.....very rapid and efficient service.
Great price. Great service. Thank you for the prompt delivery. Will definitely use again.
The team at Tank Shop have provided superior service from initial tank design and fabrication advice through to delivery and installation. I would not hesitate in recommending them for tank supplies.
Excellent communication, and quick delivery. I would buy from them again.
Great job guys, right product, right price and fast delivery. I really can't ask for too much more!!
Very helpful staff and professional service.
Great product- screen for tank. Delivery was very fast. Communication excellent.
Great service and willing to help to get minor changes done for my order
Super fast service and delivery. Excellent.
Product as advertised, fast prompt delivery. No problems at all!
Great service and products
Knowledgeable and prompt response. Great service!
Excellent service & communication
good service, quick delievery
Great - very easy.
The Tank Shop were excellent at despatching an online order in an efficient manner to Norfolk Island and the goods arrived in good condition. We were very pleased with the service received.
Great service and even better prices!
Great products and great service to back it up
Great product (Maelstrom Filter System), has made a big difference
Excellent service and value for money - Reviewed at least five tank suppliers and then found Tank Shop offering excellent deal on Qtank. Helpful and courteous dealing with both companies to get delivery tied in with other work being done. Highly recommend Tank Shop and their Qtank supplier for all aspects of purchase including delivery.
Had to get a new water tank and found this Brisbane based company online. The tank was ordered easily using the online form and payment system. The company communicated with us at every step, and delivery was definitely in the time frame they advised. The delivery guys were polite and efficient. Def recommend this company.
Got 3 tanks and 3 Maelstrom filter in 2020 in Melbourne. Very happy with kind and honest service & quick reply from Scott. Thanks
Good communication with Tank Shop made for an easy transaction. My new high quality rainwater tank and fittings arrived on schedule and the delivery driver had the tank sited in a matter of minutes. A very satisfied customer!
Excellent customer service over and above the expectation. Professional and prompt Ordering through to Delivery, Keith even helped us position the tank in which was a tricky spot. I had also initially made an error with the online payment and sent the money to a wrong Account, Scott was very helpful and we tracked the funds through Scott's Bank, CUA, no thanks to my Bank the NAB! All in all an excellent outcome, thanks Tank Shop.
My first time using Tankshop, and it all went extremely well very satisfied with pricing, quality and speedy delivery. Would recommend this seller anyone.
I ordered a $20 item plus transport from Tank Shop.
It arrived in Melbourne 2 days later and sat in the transport company’s warehouse for 2 weeks, waiting for delivery 15km away! Malessa at Tank Shop rang and emailed them each day of the second week, along with my emails to them to speed up delivery. Tank Shop offered a replacement item, sent by another transport company the day before the item arrived. Really? For the few dollars profit on my sale, Tank Shop’s customer service is like nothing I’ve experienced. Absolutely brilliant!! 12/10
Top equipment. Easy to buy and fast delivery. We keep coming back.
As I am in country NSW it was so easy to contact them, get the items I needed and the quick delivery.
I purchased a 5000l tank from the website. I had a follow up phone call that same day. Very happy with price and service received.
The Tank Shop was FANTASTIC to deal with!!!! I was VERY concerned about purchasing a tank online, so I called the number numerous times and asked 1000 questions, and the gentleman I spoke to was ALWAYS sooooo lovely and understanding of my concerns. Anyway we went with it and had our tank delivered PERFECTLY on time, with ALL the attachments we needed to make it all come together beautifully - SOOOOOO happy. I recommend you to EVERYONE! THANKS SOOOOO MUCH! WHAT CHEAP and FANTASTIC tanks!!!!
Purchased 10000L tank to take advantage of Council Rebate Scheme. Tank was delivered as arranged, driver was helpful with placing tank. Happy as Larry with the service.
Very helpful. Answered my 3 different emails regarding the Maelstrom tank filter within a number of minutes, on each occasion. I purchased it on line, & yes it fitted perfectly. Many thanks Scott.
Excellent service with prompt dispatch of goods. Very competitive pricing on all products. Highly recommended.
Very helpful, and quick to dispatch the rain catchers I needed. The price was very reasonable too.
Excellent service, found me the rain heads I wanted even though they aren't made any more.
Quick and easy, good prices. Really easy to deal with. Accidentally mistyped my address so I emailed them. They rang me and corrected it. Parcel delivered first time to the right address - brilliant.
Great service. Got exactly what we wanted when we wanted it.
Easy to deal with and did what they said they would do at a very cheap sale price.
Good to deal with.
Fast and courteous service.
Great product, fast delivery. Thank you
Fantastic service and supply in a difficult situation.
Great prices, good service, fast delivery what more can you ask for.
Quick postage, smooth transaction.
Very quick service and best price I could find.
Easy ordering process and dealing with Scott was great. Ordered a pump on the Monday and was able to pick it up on Wednesday (waiting for bank transfer to clear).
Great advice and service - Rang to get advise on a submersible pump for a tank the advice was spot on so went on the website ordered the pump at a great price and it arrived within 2 days.
Great service, great product.
Very friendly and informative right from the first call asking for tank options and prices. Delivery of my tank was very quick.